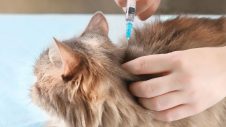
We highly recommended vaccinations as an essential factor for your cat’s ongoing health. Vaccinations protect your cat from contagious and preventable disease. Some of these diseases can be fatal and many don’t have a cure, so vaccinating your cat is very important to keep them safe and healthy.
Which diseases do vaccinations help protect my cat from?
The F3 vaccine provides protection against the following three viruses. This is referred to as a ‘core vaccine’ in Australia.
1. Feline Panleukopenia Virus
2. Feline Herpes Virus
3. Feline Calicivirus
In addition to the above, for cats that are outdoors, unsupervised and could potentially interact/fight with other cats, it is worth discussing protecting your cat with the following non-core vaccinations.
4. Chlamydophila felis
5. Feline Leukemia Virus
6. Feline Immunodeficiency Virus (FIV)
View our recommended cat vaccination schedule here.
More information about these diseases
Protected against by core vaccine
1. Feline Panleucopenia virus (also known as feline parvovirus or feline infectious enteritis) can cause severe haemorrhagic gastroenteritis. The virus is highly contagious amongst cats, and it can survive in the environment for long periods of time, making vaccination against it important.
2. Feline Herpes Virus causes upper respiratory signs in cats, such as sneezing, nasal discharge, conjunctivitis, ocular discharge, pharyngitis, inappetence, lethargy, and fever. It can also cause keratitis (inflammation +/- infection of the eye surface) with chronic infection. FHV is transmitted by direct contact (saliva, ocular and nasal discharge), inhalation of infected droplets in the air from sneezing, sharing food/water bowls and from the environment.
3. Feline Calicivirus causes upper respiratory signs in cats and can have very similar signs to Feline Herpes Virus (FHV). As well as respiratory signs, cats may also experience oral ulceration, excessive drooling, gingivitis, stomatitis and in very young kittens, pneumonia. FCV is transmitted by direct contact (saliva, ocular and nasal discharge), inhalation of infected droplets in the air from sneezing, sharing food/water bowls and from the environment.
Protected against by non-core vaccinations
4. Chlamydophila felis is a bacterium that can cause conjunctivitis, ocular infections, nasal discharge and sneezing. It is predominantly contracted via direct contact with other cats, as it does not survive well in the environment.
5. Feline Leukemia Virus causes immunosuppression in affected cats, making them significantly more likely to succumb to other diseases. Infected cats are at greater risk of developing anemia, developing cancers, such as lymphoma, leukemia and some other tumours. This virus is transmitted predominantly through saliva, but can also be shed in urine, faeces, and milk.
FLV can be spread by social contact (eg. mutual grooming, sharing food/water bowls and litter trays), has the potential to spread from bite wounds and it is a very high risk for a mother cat to pass on to her kittens (if they survive till term at all, as many mother cats will lose the kittens before birth, if they have this disease). It is estimated that about 1-2% of the cat population in Australia is infected with the virus.
6) Feline Immunodeficiency Virus (FIV) also causes significant immunosuppression. It is transmitted predominantly through bite wounds (saliva containing the virus, being directly injected into the blood stream of a non-infected cat). It can also be transmitted from blood to blood, sexually transmitted and there is a chance of it being passed from mother to kitten. FIV cannot survive long out of the body, so it is rare to contract it indirectly from the environment, shared food/water bowls, mutual grooming between cats, etc.
It is estimated that ~15% of cats across Australia are suspected to have this disease, but reports range from 7%-30% of the cat population, depending on the location and stray vs owned cats, around Australia.

 Greencross Vets
Greencross Vets